Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-11-23 Origin: Site
An aneroid sphygmomanometer blood pressure cuff is a popular alternative to the traditional mercury monitor, offering portability and safety without sacrificing reliability. If you’ve ever wondered what is the difference between an aneroid and mercury sphygmomanometer, this guide will walk you through key features, accuracy, and practical use. Understanding these differences helps healthcare professionals, home users, and clinics choose the right device for accurate blood pressure measurement. Explore how aneroid and mercury sphygmomanometers compare in daily practice, calibration needs, and overall convenience.
Understanding blood pressure starts with one essential tool—the sphygmomanometer. It’s the device doctors, nurses, and millions of people worldwide use to check how hard the heart pushes blood against artery walls. A sphygmomanometer usually includes a cuff, a pressure-measuring unit, and a way to inflate the cuff. The design seems simple, but the accuracy of this device matters more than most people realize.
A sphygmomanometer measures systolic and diastolic pressure in a non-invasive way. You’ve probably seen one in clinics: a cuff wraps around the upper arm, inflates, and temporarily stops blood flow. As the air slowly releases, the device detects pressure changes. Its job is to show the numbers that help diagnose hypertension, monitor treatment, and track cardiovascular risk. Without a reliable measurement, doctors can’t make the right decisions.
Blood pressure shifts during daily activity. Stress, movement, or even talking can change the reading. Inaccurate measurements may lead to:
Misdiagnosis of hypertension or hypotension
Incorrect medication dosage
Missed early warning signs
False reassurance for high-risk patients
Small errors—sometimes only a few millimeters of mercury—can influence treatment plans. That’s why the type of blood pressure device we choose plays such an important role.
Today, three major sphygmomanometer types are widely used. Each works differently, and each has strengths and limits.
| Type of Device | How It Measures | Accuracy Level | Common Users | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mercury Sphygmomanometer | Mercury column + auscultation | ★★★★★ (Gold standard) | Hospitals, research | Highly stable; no calibration needed |
| Aneroid Sphygmomanometer | Mechanical dial + auscultation | ★★★★☆ (High, but varies) | Clinics, home nurses | Needs calibration; portable |
| Digital Sphygmomanometer | Electronic sensors + oscillometry | ★★★☆☆ (Good for general use) | Home users | Very easy to use; less accurate for certain conditions |
Mercury devices are disappearing because of global environmental rules. Hospitals want safe, accurate alternatives that don’t expose people to mercury. Aneroid sphygmomanometers have become the natural replacement. But they work differently, need maintenance, and respond differently to shock or wear. Understanding the differences helps clinics, caregivers, and home users choose a device that gives trustworthy readings every time.
Mercury sphygmomanometers are classic tools used to measure blood pressure. They rely on simple physics but deliver precise results. Many healthcare professionals still consider them the benchmark for accuracy.
A mercury sphygmomanometer uses a column of mercury to indicate pressure. The cuff wraps around the upper arm and inflates until blood flow temporarily stops. As the cuff slowly deflates, we listen for Korotkoff sounds using a stethoscope. These sounds mark the systolic and diastolic pressures. The height of the mercury column directly corresponds to the blood pressure reading in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). This auscultatory method requires attention and careful technique.
Considered the gold standard for blood pressure measurement
Stable readings unaffected by small mechanical errors
No calibration needed due to physical properties of mercury
Simple, mechanical design with minimal moving parts
| Feature | Mercury Device | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Very high | Often used in research and clinical trials |
| Calibration | Not required | Mercury column provides natural reference |
| Durability | Long-lasting | Minimal maintenance needed |
| Complexity | Manual | Requires training to read Korotkoff sounds |
Unmatched accuracy in clinical and research settings
Reliable over decades, rarely affected by mechanical wear
Ideal for validating new blood pressure devices
Consistently trusted for high-risk patient monitoring
Mercury is toxic, posing health hazards if spilled
Environmental laws are phasing out mercury in many countries
Heavy and less portable, unsuitable for home or field use
Breakage can cause contamination, requiring careful handling
Mercury sphygmomanometers remain a symbol of precision. Despite environmental concerns, they provide the benchmark against which other devices are measured.
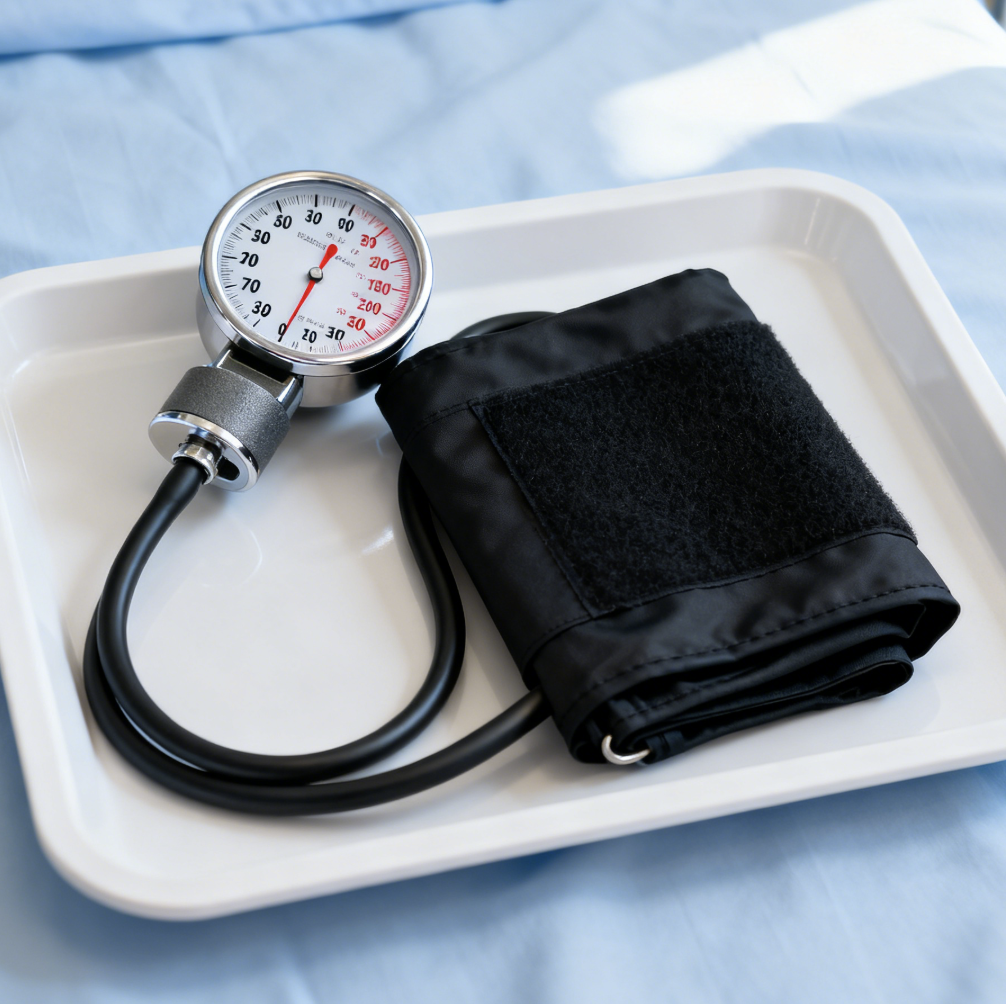
Aneroid sphygmomanometers are widely used alternatives to mercury devices. They use mechanical components instead of liquid mercury, making them safer and more portable.
An aneroid sphygmomanometer blood pressure cuff features a dial gauge with a needle that moves across a scale. It relies on springs and gears to translate cuff pressure into a readable value. The cuff is inflated around the upper arm, and a stethoscope is used to detect Korotkoff sounds, just like in mercury devices. This mechanical system measures the force of blood flow and displays it clearly on the dial.
Lightweight and portable, easy to carry between clinics
Mercury-free, environmentally safe
Often includes a built-in or separate stethoscope for auscultation
Mechanical design allows simple operation for trained users
| Feature | Aneroid Device | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Portability | High | Ideal for field and clinic use |
| Accuracy | High if calibrated | Must check regularly |
| Safety | Mercury-free | Reduces environmental hazard |
| Durability | Good | Sensitive to mechanical shock |
High accuracy when calibrated properly
Cost-effective alternative to mercury devices
Durable and portable, suitable for multiple settings
Easy to train medical staff to use correctly
Requires regular calibration to maintain accuracy
Prone to mechanical damage if dropped or jarred
Accuracy depends heavily on user skill and technique
Slightly less precise than mercury devices under certain conditions
Aneroid sphygmomanometers provide a reliable balance of accuracy, portability, and safety, making them popular in clinics, schools, and home settings.

Understanding the differences helps choose the right blood pressure device for clinics, fieldwork, or home monitoring.
Mercury sphygmomanometers deliver the highest precision, often called the gold standard.
Aneroid devices are accurate only if calibrated regularly.
Industry guidelines like AAMI and ESH recommend periodic verification for aneroid devices.
Mercury devices require minimal calibration, often stable for decades.
Aneroid devices need periodic calibration due to mechanical wear and tear.
Skipping checks can lead to inaccurate readings, especially in clinical trials.
Mercury is toxic, with potential hazards if the device breaks.
Aneroid devices are mercury-free, safe for transport and home use.
Environmental regulations are increasingly restricting mercury devices globally.
Mercury devices are heavy and fragile, not ideal for travel.
Aneroid devices are lightweight, compact, and travel-friendly, easy to carry between rooms or clinics.
Mercury sphygmomanometers are mechanically stable, but breaking the glass can cause contamination.
Aneroid devices are sturdy but sensitive to drops or shock.
Both need careful handling to maintain reliability.
Both types require trained personnel for accurate readings.
Aneroid models are sometimes easier for fieldwork, as they are lighter and don’t rely on liquid columns.
Mercury sphygmomanometers are more expensive, and fewer suppliers exist.
Aneroid devices are affordable, widely available, and suitable for clinics with limited budgets.
Many countries are phasing out mercury devices due to health risks.
Hospitals follow national regulations for medical equipment.
WHO recommends mercury-free devices where possible.
| Feature | Mercury Sphygmomanometer | Aneroid Sphygmomanometer |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Highest | High if calibrated |
| Calibration | Minimal | Regular required |
| Safety | Mercury risk | Mercury-free, safe |
| Portability | Heavy, fragile | Lightweight, portable |
| Durability | Stable but breakable | Sturdy, shock-sensitive |
| Ease of Use | Needs trained user | Easier in fieldwork |
| Cost | Expensive | Affordable |
| Regulation | Restricted in many countries | Widely accepted |
Mercury sphygmomanometers are still valued for their precision and reliability. Certain situations make them the preferred choice.
Often used as a reference standard in clinical trials.
Provides consistent readings for comparing new blood pressure devices.
Essential when regulatory or scientific accuracy is required.
Common in cardiology clinics and specialized medical departments.
Used for patients needing close blood pressure monitoring.
Favored when long-term measurement stability is critical.
Cases like hypertension evaluation, pre-surgical assessments, or critical care.
Mercury devices minimize observer bias and instrument errors.
Important when even small variations in blood pressure affect treatment decisions.
Used to train medical students and nurses in auscultatory technique.
Allows learners to hear Korotkoff sounds accurately.
Serves as a benchmark for comparing manual and digital devices.
| Setting | Why Mercury Is Preferred |
|---|---|
| Research | Gold standard for validation |
| Professional clinics | Stable, reliable readings |
| Critical care | Highest accuracy for decisions |
| Teaching hospitals | Teaches correct auscultation |
Aneroid sphygmomanometers are versatile and practical. They are ideal for situations where portability, safety, and ease of use matter.
Perfect for routine blood pressure checks in hospitals and clinics.
Lightweight design allows frequent use without strain.
Can be paired with a stethoscope for manual auscultation.
Compact and easy to carry to patients’ homes.
Enables nurses and community health workers to monitor blood pressure efficiently.
Safe for settings where mercury devices are impractical.
Suitable for fieldwork, ambulances, and disaster zones.
Durable design withstands movement and transport.
Quick setup supports rapid patient assessment.
Many facilities ban mercury devices due to environmental and safety rules.
Aneroid devices provide a reliable alternative.
Meets hospital safety policies while maintaining accuracy.
| Setting | Why Aneroid Is Preferred |
|---|---|
| Daily clinics | Lightweight and practical |
| Home visits | Portable for fieldwork |
| Emergency care | Durable, easy to deploy |
| Mercury-restricted clinics | Safe, compliant alternative |
Yes. Mercury devices are gradually replaced globally due to toxicity concerns and environmental regulations. Some hospitals still use them for research or validation purposes.
Aneroid devices can be very accurate when properly calibrated and maintained. Mercury devices are the gold standard, but well-maintained aneroid sphygmomanometers offer reliable readings.
Calibration is recommended at least once a year or more if used heavily. Frequent checks ensure consistent accuracy and reliable readings.
Aneroid and digital devices are ideal for home use. They are safe, portable, and easy for non-professionals to operate. Mercury devices are generally unsuitable at home.
Digital devices are convenient but may be less accurate than mercury or well-calibrated aneroid devices. Proper calibration and technique are key for trustworthy readings.
Choosing the right blood pressure device comes down to understanding how each works and what fits your needs. Mercury sphygmomanometers offer unmatched precision, while aneroid models bring portability, safety, and ease for everyday use. Both have strengths, and using them correctly ensures accurate, reliable readings every time.
At RUIAN SUNNYWORLD INTERNATIONAL TRADE CO., LTD, we provide high-quality aneroid and digital sphygmomanometers that meet clinical standards and home care needs. Explore our range to find the perfect device for your practice, community program, or personal monitoring. Accuracy, safety, and convenience all in one.
