Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-10-22 Origin: Site
When it comes to measuring blood pressure, two types of sphygmomanometers—aneroid sphygmomanometers and mercury sphygmomanometers—are commonly used in healthcare settings. Both instruments perform the same function: measuring the force of blood against the walls of arteries. However, they operate in very different ways, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
In this article, we will delve into the differences between the aneroid sphygmomanometer and mercury sphygmomanometer, highlighting their features, accuracy, and use cases. By the end of this article, you'll have a better understanding of which device is best suited for your needs, whether you're a healthcare professional or an individual monitoring blood pressure at home.
An aneroid sphygmomanometer is a manual device used to measure blood pressure without the use of mercury. Unlike the mercury sphygmomanometer, which uses a liquid mercury column to measure pressure, the aneroid version uses a dial gauge connected to a pressure cuff that inflates around the patient's arm. The device is widely used in hospitals, clinics, and at-home settings due to its portability, safety, and ease of use.
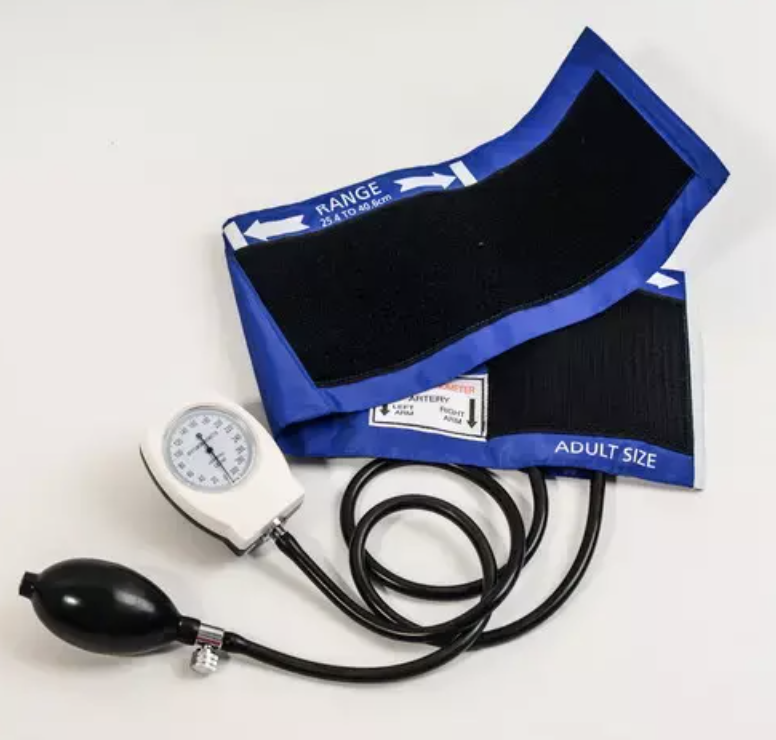
Pressure Cuff: Wraps around the upper arm to temporarily halt blood flow.
Dial Gauge: Measures the pressure exerted on the artery walls, displayed in millimeters of mercury (mmHg).
Inflation Bulb: Manually inflates the cuff to apply pressure on the artery.
Release Valve: Allows controlled deflation of the cuff to release the pressure gradually.
Stethoscope: Used by the healthcare provider to listen for the sounds of blood flow as the cuff deflates.
A mercury sphygmomanometer is the traditional and highly accurate blood pressure measuring device that uses a column of mercury to determine blood pressure. This device was the standard for many years before being largely replaced by digital and aneroid models due to safety and environmental concerns.
Mercury Column: The height of the mercury column rises or falls based on the pressure exerted by the blood, indicating systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Pressure Cuff: Similar to the aneroid version, it wraps around the arm to temporarily stop blood flow.
Inflation Bulb: Inflates the cuff to exert pressure on the artery.
Release Valve: Releases the air gradually, allowing for measurement of systolic and diastolic pressures.
Both the aneroid sphygmomanometer and mercury sphygmomanometer are widely used for measuring blood pressure, but they rely on different mechanisms and offer distinct advantages and disadvantages. Below, we compare these two types of blood pressure measurement devices based on several factors including accuracy, safety, cost, portability, and maintenance requirements.
Mercury Sphygmomanometer:
The mercury sphygmomanometer is often considered the gold standard in blood pressure measurement due to its exceptional accuracy and reliability. The device’s mercury column directly measures the pressure in the arteries, ensuring precise and consistent readings every time.
Why it's accurate: The mercury column is a simple and direct method for measuring blood pressure, which eliminates the potential for discrepancies. Since mercury sphygmomanometers rely on a visible column of mercury, healthcare professionals can interpret the readings with great precision.
Longevity of accuracy: Once properly calibrated, mercury models can continue to provide accurate readings for extended periods, without the need for frequent recalibration.
Aneroid Sphygmomanometer:
The aneroid sphygmomanometer, while capable of providing accurate readings, is more sensitive to calibration and maintenance. Over time, the mechanical parts may shift, leading to slightly less reliable results if the device isn't properly maintained.
Why it’s less accurate: While aneroid devices also measure pressure with a dial gauge, their accuracy is dependent on the calibration and care taken in the device’s handling. Without regular recalibration, aneroid gauges can lose their accuracy, leading to potential misreadings.
Mercury Sphygmomanometer:
One of the main drawbacks of the mercury sphygmomanometer is the environmental and health risks associated with mercury. If the device is dropped or improperly disposed of, mercury can leak, creating toxic exposure hazards both to people and the environment.
Mercury hazards: Exposure to mercury can lead to serious health problems, including neurological damage. This risk has led many countries to ban or restrict the use of mercury sphygmomanometers in favor of safer alternatives.
Environmental concerns: Since mercury is a toxic heavy metal, improper disposal or accidental breakage can result in environmental pollution. As a result, mercury sphygmomanometers are being phased out in many clinical settings worldwide.
Aneroid Sphygmomanometer:
Aneroid sphygmomanometers are safer and more environmentally friendly because they do not use mercury. This makes them a preferred option for settings that prioritize sustainability and safety.
No hazardous materials: Since the device uses a mechanical spring mechanism rather than mercury, it eliminates any risk of exposure to toxic substances, making it both user and environmentally safer.
Less waste: The absence of mercury also ensures that aneroid sphygmomanometers have minimal environmental impact, which is crucial for healthcare facilities aiming to be eco-friendly.
Mercury Sphygmomanometer:
Mercury sphygmomanometers are generally more expensive due to the precise and specialized manufacturing process involved in producing the mercury column. This added complexity translates to higher production and retail prices.
Higher price point: For healthcare providers or individuals with limited budgets, the mercury sphygmomanometer might be out of reach due to its relatively high cost compared to other models.
Aneroid Sphygmomanometer:
Aneroid sphygmomanometers are more affordable, primarily because they don’t require the mercury column and have a simpler mechanical design. This makes them an attractive option for both home use and healthcare providers working with budget constraints.
Affordable and accessible: The aneroid sphygmomanometer is generally more accessible, offering cost-effective options without sacrificing much in terms of accuracy when properly calibrated.
Mercury Sphygmomanometer:
Mercury sphygmomanometers are relatively bulky and fragile. The glass mercury column is prone to breaking, and the device is typically heavier compared to its aneroid counterpart.
Limited portability: Due to their weight and fragility, mercury models are not ideal for use in mobile healthcare settings or environments where frequent transport is required.
Storage concerns: The glass column also makes mercury sphygmomanometers difficult to store safely. It is essential to handle them with care to prevent any damage.
Aneroid Sphygmomanometer:
Aneroid sphygmomanometers are lightweight, portable, and more durable than mercury sphygmomanometers. Their design allows for easy handling and storage, making them ideal for use in various healthcare environments.
Portability: The compact nature of the aneroid sphygmomanometer makes it suitable for use in mobile clinics, home visits, and places where space is limited, such as narrow aisle electric forklifts or smaller medical practices.
Convenient storage: These devices can be safely stored in compact spaces without the worry of damaging fragile components.
Mercury Sphygmomanometer:
Mercury sphygmomanometers are very durable and require minimal maintenance. Once set up, they tend to remain accurate for many years without needing regular recalibration.
Low-maintenance: If the device is carefully handled and stored in a safe place, it will not require frequent calibration, making it very reliable in the long term.
Aneroid Sphygmomanometer:
The aneroid sphygmomanometer requires regular calibration to ensure consistent accuracy. As the device ages, the mechanical components may shift or wear down, which can affect the readings if not properly calibrated.
Periodic checks: Regular maintenance by trained professionals is essential for maintaining aneroid sphygmomanometers. Frequent checks are required to avoid any errors in blood pressure measurement.
Choosing between an aneroid sphygmomanometer and a mercury sphygmomanometer depends on your specific needs and preferences. Here’s a quick guide to help you decide:
If you need extreme accuracy and are working in a controlled clinical environment, a mercury sphygmomanometer might be the best choice.
If portability, safety, and cost are your priorities, the aneroid sphygmomanometer is a more practical and safer option, especially for home use or mobile healthcare providers.
Environmental concerns: If you are concerned about the environmental impact of mercury, an aneroid sphygmomanometer is a far safer and more sustainable choices.
| Feature | Aneroid Sphygmomanometer | Mercury Sphygmomanometer |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | High (with proper calibration) | Very high (gold standard) |
| Safety | Mercury-free, safe | Potential mercury hazard |
| Portability | Lightweight and portable | Heavy and fragile |
| Cost | Affordable | Expensive |
| Environmental Impact | Environmentally friendly | Mercury poses environmental risk |
| Maintenance | Requires calibration | Low maintenance |
| Durability | Moderate (mechanical components) | High (glass mercury column) |
Mercury sphygmomanometers are generally considered more accurate, as they directly measure pressure with the mercury column. However, with proper calibration, an aneroid sphygmomanometer can also provide highly accurate readings.
Mercury sphygmomanometers are being phased out due to the environmental and health hazards associated with mercury. The toxic nature of mercury can cause serious environmental damage if the device is broken or improperly disposed of.
Yes, aneroid sphygmomanometers are ideal for home use because they are portable, cost-effective, and safe. However, users should ensure proper technique and calibration to get accurate readings.
It is recommended to calibrate your aneroid sphygmomanometer annually or more frequently if it experiences significant wear or mechanical issues. Regular calibration ensures accurate readings.
Yes, digital blood pressure monitors are an alternative. These devices are easy to use, but they are generally considered less accurate than the mercury sphygmomanometer and sometimes less durable than the aneroid sphygmomanometer.
Choosing between an aneroid sphygmomanometer and a mercury sphygmomanometer depends on various factors, including accuracy, safety, cost, and intended use. While the mercury sphygmomanometer is the gold standard for accuracy, the aneroid sphygmomanometer is a reliable, cost-effective, and eco-friendly option, especially for home use and mobile healthcare providers.
If you're looking for a high-quality aneroid sphygmomanometer, consider visiting sunnyworld, where we offer a wide range of durable and affordable blood pressure monitoring devices designed for both personal and professional use.
By understanding the differences between these two types of sphygmomanometers, you can make an informed choice that best fits your needs, ensuring accurate blood pressure readings and better overall health management.
